
.NET Developer
.NET developer is a software engineer who builds the software using Microsoft’s .NET technologies. He is responsible for the design, implementation and development of the software products according to technical needs.
Table of contents
- What is .NET?
- History and Interesting Facts
- Number of websites created with .NET worldwide
- .NET Products
- Technologies Stack
- Why to choose .NET
- .NET Market Situation
- Demand on .NET Developers
- What is a .NET developer
- .NET Developer Portrait
- .NET Developer Experience levels
- .NET Developer’s salary
- Typical Tasks For .NET Developers
- Requirements for .NET Developers
- What is Important to Know for Hiring .NET Developers?
- How to Hire a Certified .NET Developer?
- Most common problems for the .NET developers
- How to Become .NET developer
- Additional knowledge areas for .NET developers
- Education
- Career change
- Certifications
- .NET Community Events 2024
- .NET Developer CV/Resume
What is .NET?
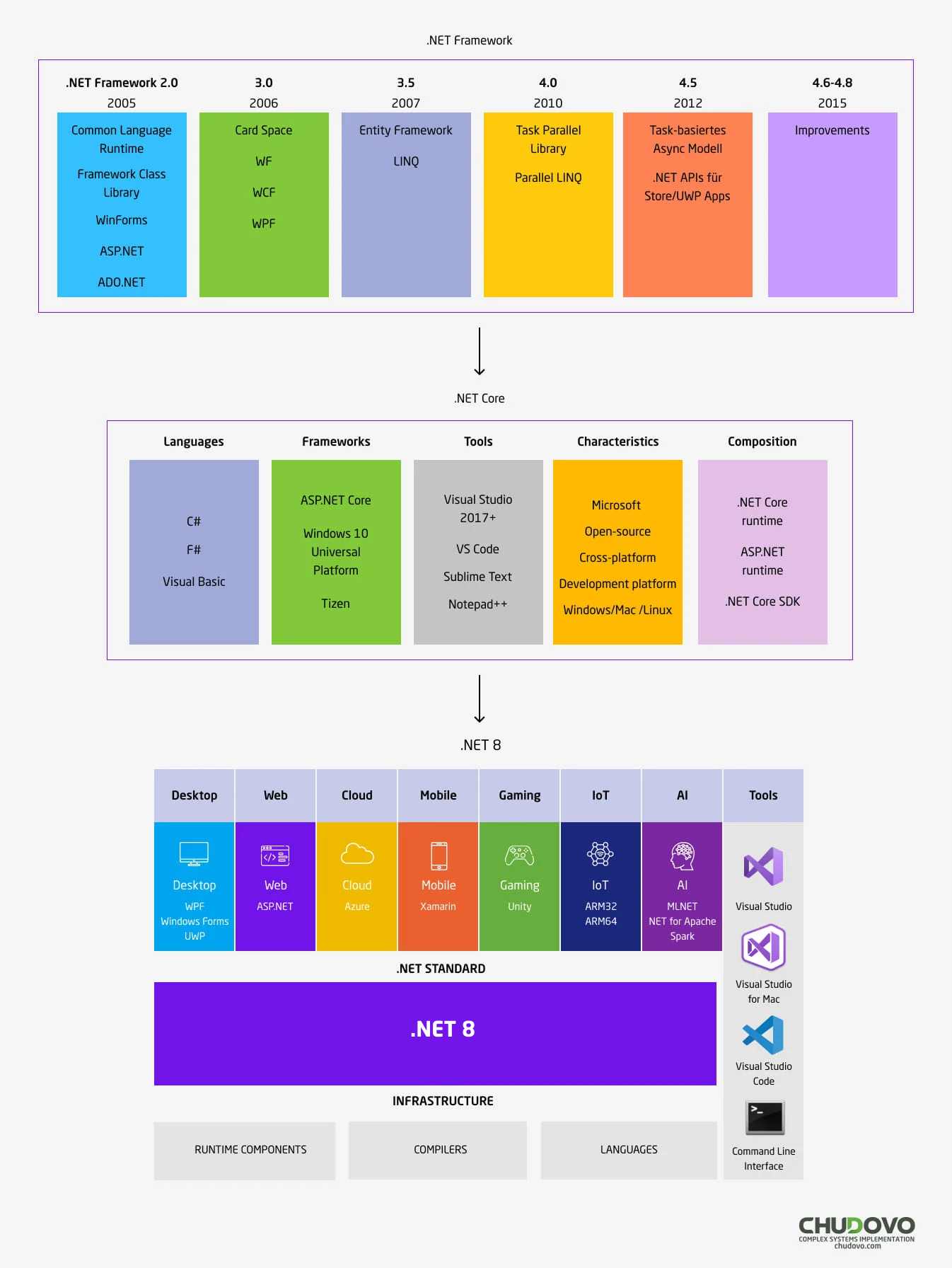
.NET Framework is the original realisation of .NET, it is a software development framework for building the applications. It can be launched on Windows. .NET Framework is a collection of the technologies for creation of the applications for Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Android etc.
.NET Core is a cross-platform open-source framework for building the applications. It is a new interpretation of .NET Framework that can be launched across different operating systems and enables the development of the applications for various platforms.
.NET is a unified .NET platform for building the applications. It is a new generation of Microsoft’s .NET Core. .NET 8 is an open-source platform for the development of software such as web, mobile, desktop applications, IoT, and games for different OS.
History and Interesting Facts
Unofficially the development of .NET Framework started in 1999. The official announcement about the development of new technology took place at the Microsoft press conference on the 13th of January, 2000. On this date Bill Gates handed over the management of the software company to Steve Ballmer. Gates retained the post as chairman and added an additional title as chief software architect. To summarize Steve Ballmer said that Microsoft has an incredible opportunity to revolutionize the Internet user experience. In order to do that they will deliver the next generation services platform. So Bill Gates should be 100 percent focused on helping architect that.
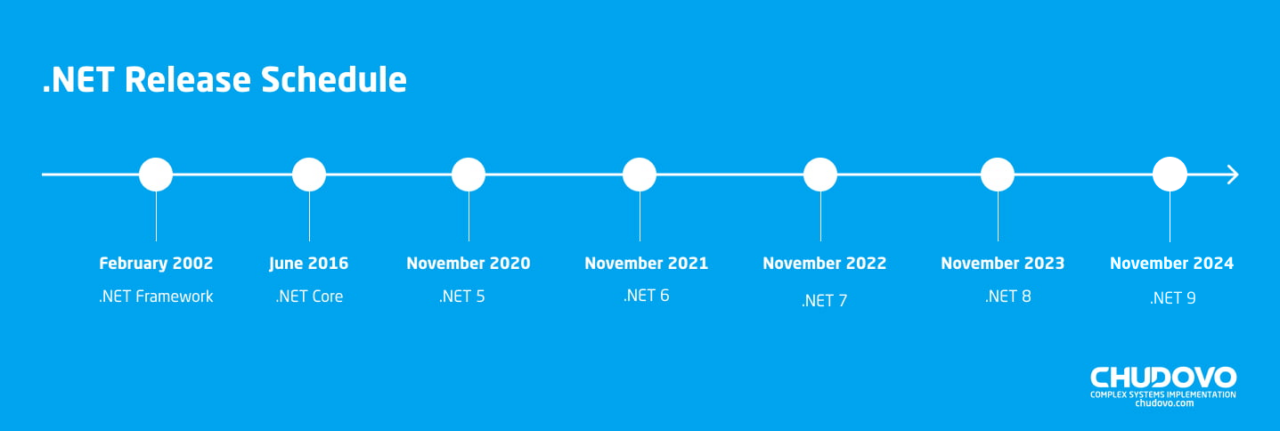
Finally, after a few years of active development the world saw this revolutionary platform. The first version of Microsoft .NET Framework was officially released on the 13th of February, 2002. Since the release of the first .NET Framework version nine more upgrades took place. The final version of .NET Framework was 4.8.
.NET Core is an open-source, cross-platform framework (Windows, Mac, Linux) that can be defined as a successor to .NET Framework. It is a modern analogue of the .NET Framework. Microsoft announced development of .NET Core on 12th of November, 2014. .NET Core had an official release on 27th of June, 2016. Microsoft updated .NET Core and released its new versions till 3.1. However, in November 2020 the newest version of .NET Core was shipped as .NET 5. “Core” was removed from the name and version 4.0 was skipped to avoid the confusion with .NET Framework.
.NET 8 is the next major November 2023 upgrade of the .NET platform. Microsoft has already published .NET 8 and it could be downloaded from the official Microsoft website. According to the information the release of dot NET 9 is planned for November 2024. The most relevant updates as well as news about .NET 8 can be found in official Microsoft’s documentation.
Interesting facts
We’ve gathered a few interesting facts about Microsoft’s .NET technology that might be interesting to know about:
Fact 1. Initially the Microsoft .NET Framework was developed under the strategy with the naming NGWS. The abbreviation means Next Generation Windows Services.
Fact 2. Developers can launch .NET Framework on Windows 10 and its earlier versions, other operating systems are not foreseen. In contrast to .NET Framework with limited Windows 10 and earlier versions option, .NET Core runs on different operating systems – Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Fact 3. Using Microsoft’s .NET technologies it is possible to create the applications for several platforms and in different variations:
- Back-end and Front-end applications development
- .NET Web applications development
- .NET Mobile applications development
- .NET Desktop applications development
It is also possible to produce the games and simulations as well as IoT apps.
Fact 4. From the point of view of the architecture .NET applications are created based on Monolithic architecture or Microservies architecture. Monolithic approach is a more traditional way of building applications and in this context the software is produced as one single unit. Nowadays microservices are becoming popular and it is a trend. In this model all the services are created as separate units, which communicate via messaging.
Fact 5. The .NET Framework is believed to have been Microsoft’s response to the then-popular Java platform from Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle). C# language was a Java clone on the initial stage.
Number of websites created with .NET worldwide
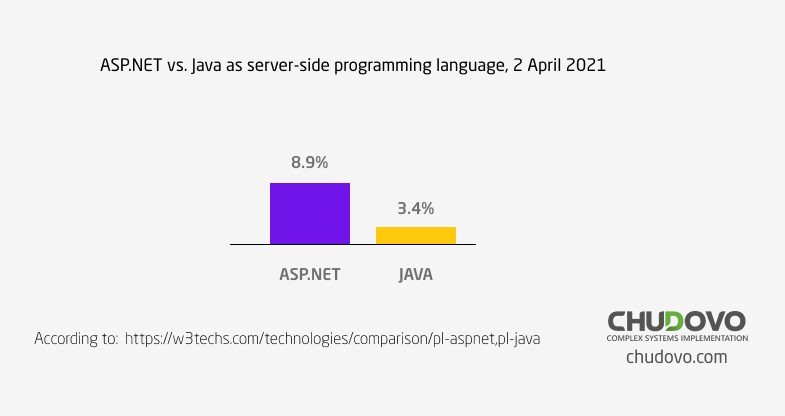
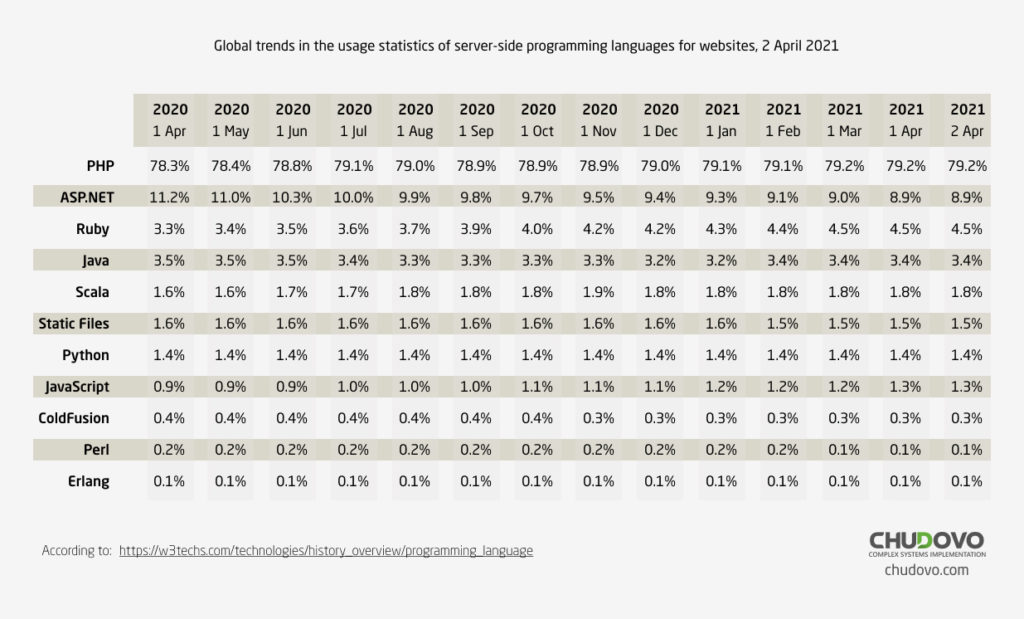
.NET development technologies are widely used for creation of the software. W3techs, Web Technology surveys, carried out a research and reported the statistic of ASP.NET vs. Java usage as the server-side web programming language. Dated on 2rd of April 2021, It was determined that 8,9% of all the websites are using ASP.NET as server-side programming language and only 3,4% are using Java. So, .NET web development is quite popular.
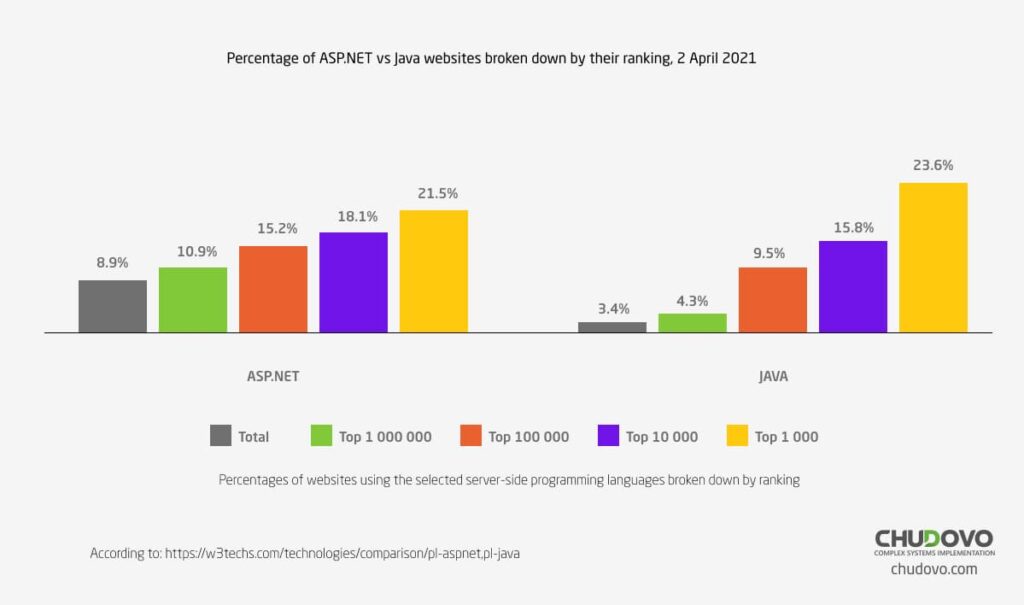
The provider of tech surveys also gives the information about the percentage of ASP.NET vs. Java on the websites broken down by their ranking in form of a comparison diagram. The bar chart demonstrates a distribution dated on 2rd of April, 2021. The most noticeable thing about the graph is that ASP.NET is used by 10,9% of the websites that are ranked in the top million.
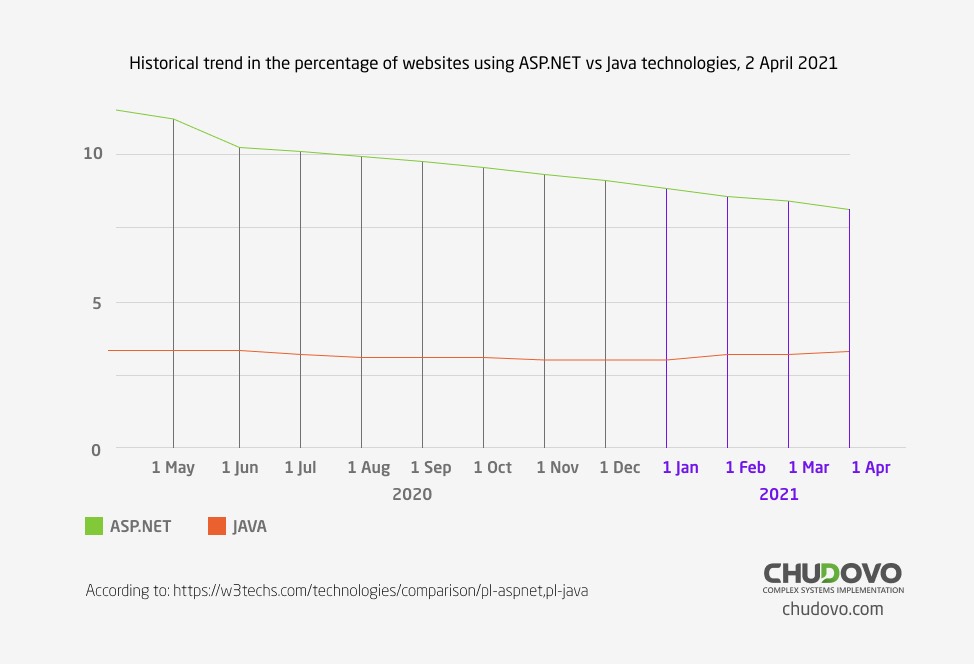
During the investigation web technology surveys provider has also visualized the historical trend in the ASP.NET vs. Java percentage of usage by the websites as server-side programming language. The graph represents how the usage has been changed over time. If we look at this line chart we can make the conclusion that the popularity of .NET web development is quite high.
W3techs has also made an investigation in the direction of the global trends and shared the statistics of mostly user server-side programming languages for the websites. Statistical data clearly shows that ASP.NET takes the second place and has a valuable market share percent.
.NET Products
.NET Framework vs. .NET 8 (including .NET Core) for server apps
.NET server-side applications can be developed in two supported implementations: .NET 8 0(including .NET Core) and .NET Framework. They share many same components and the code can be shared across both. Although, between these two environments there are differences and the choice depends on the business needs.
When to choose .NET 8 for the server application:
- Need in cross-platforming. If you need to create an application (web application or service) with support for different platforms (Windows, macOS or Linux), .NET 8. is the best choice.
- Microservices architecture. Microservices architecture enables the technologies mix across the service boundary. This combination of technologies allows new microservices to be gradually added to .NET 8 for concurrent use with other microservices and services. For instance, it is possible to combine microservices or services built on .NET Framework, Java, Ruby or other monolithic technologies.
- Docker containers. Containers are commonly used along with the microservices architecture. The lightweight nature and modularity of .NET 8 make it optimal for containers. By creation and deployment of the container, its image size is much smaller in .NET 8 in comparison to .NET Framework. As .NET 8 supports several OS server applications can be deployed to Linux Docker containers.
- Performance and scalability. If the system requires maximum scalability and performance, it is recommended to use .NET 8 and ASP.NET Core. High performance server runtime for Windows Server and Linux makes .NET the most efficient web framework in TechEmpower benchmarks. The topics of scalability and high-performance are especially important for microservices architectures, where several microservices may run at the same time. ASP.NET Core allows to reduce the number of servers and virtual machines that are required for the system.
- Side-by-side .NET versions per application. If it is needed to install the applications with the dependencies on different versions of the .NET, it is better to use .NET 8. .NET 8 supports side-by-side installation of different versions of the .NET 8 runtime on the same machine. With a simple side-by-side installation, multiple services can be hosted on a single server, each of which installs on its own version of .NET 8 (or .NET Core 2.1 or 3.1). This eliminates risks and reduces the cost of application updates and IT operations.
Undoubtedly. Microsoft .NET 8 provides several benefits for the new apps and application pattern. Nevertheless, the .NET Framework remains a good choice in many situations. That’s why .NET 8 cannot replace .NET Framework for all types of server-side apps.
When to choose .NET Framework for the server application:
- The existing app is already on .NET Framework. In the vast majority of cases there is no need to migrate existing applications to .NET 8. As an alternative .NET 8 can be used to extend an existing app. For example, for writing a new web service using ASP.NET Core.
- In the app are used NuGet packages or third-party libraries that are not available for .NET 8. .NET Framework should only be used where libraries or NuGet packages use technologies that are not available in.NET 8 and .NET Standard.
- The app uses the technologies that are not available for .NET 8. .NET 8 doesn’t include some technologies that are available in .NET Framework. For example, ASP.NET Web Forms, ASP.NET Web Pages, Workflow-related services, WCF services implementation, Language support (f.e. F# and Visual Basic are supported only for some project types in .NET 8).
- Platform doesn’t support .NET 8. Some Microsoft and third-party platforms do not support .NET 8. Some Azure services provide SDKs that are at this moment not available in .NET 8. In this situation, REST API can be used as an alternative to the client SDK.
.NET 8 what’s new?
.NET 8 is the 4th major release of the .NET unification, which started with .NET 5 in November 2020. This release introduces new features that are very valuable for developing scalable, secure, and high-performance apps. What’s new in NET 8:
- Performance optimization
- Several enhancements for the .NET MAUI for building native desktop and mobile apps (enables creation of the applications using the same codebase)
- .NET Aspire – cloud-native stack for building distributed applications
- Several enhancements for the Entity Framework Core
- The .NET 8 SDK brought along the latest version of C#, C#12
- Some ASP.NET Core improvements that are related to SignalR, Blazor, etc.
- Small impovements for Windows Forms and WPF
Technologies Stack
User interface technologies
User interface-based applications can be divided into two categories: a thin client, which is equivalent to a website and a thick or rich client, which is a program that the end user should download and install on the computer or mobile device. The .NET platform offers the ASP.NET and ASP.NET Core frameworks for development of the thin client applications. For building rich client applications targeting the Windows 7/8/10 desktop, the .NET platform provides WPF and Windows Forms APIs. The .NET MAUI is available for building rich client apps targeting mobile devices with iOS and Android and desktop with Windows and MacOS. The UWP framework is available for writing rich Windows Store client apps that run on Windows 10 desktops and devices. Finally, there is a hybrid technology called Silverlight that has almost gone in history since the release of HTML5.
ASP.NET
What is ASP.NET? ASP.NET is an open-source framework that helps in designing web applications and services with .NET. Applications written using ASP.NET are hosted on a Windows IIS server and can be accessed from any web browser. The following are the advantages of ASP.NET over rich client technologies:
- No need for client-side deployment;
- Clients can run on platforms other than Windows;
- Easy to deploy updates.
In addition, because most of the code written in an ASP.NET application runs on the server, the data access layer is designed to function in the same application domain — without limiting security or scalability. In contrast, a rich client that does the same is usually not that secure or scalable. (In the case of a rich client, the solution involves creating a middle tier between the client and the database. The middle tier runs on a remote application server (often alongside the database server) and communicates with the rich clients through WCF, Web Services, or Remoting.)
When writing your web pages, you can choose between the traditional Web Forms API and the newer MVC (Model-View-Controller) API. Both are built on basing on the ASP.NET. Web Forms technology was part of the .NET Framework from the beginning and MVC was implemented much later. Overall, the MVC structure provides a better programming abstraction in comparison to the Web Forms. It also allows to have more control over the generated HTML markup. The only thing that MVC loses to Web Forms is the visual designer, which makes Web Forms a good tool for building web pages with predominantly static content.
ASP.NET Core
ASP.NET Core is added relatively recently and is similar to ASP.NET, but it functions in the .NET Framework and .NET Core environments (allowing cross-platform deployment). ASP.NET Core infrastructure has a modular architecture and is licensed for open source software. Unlike its predecessors, the ASP.NET Core does not depend on System.Web and lacks the historical baggage of Web Forms. It is especially well suited for microservices and intra-container deployments.
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF)
What is WPF? WPF enables the creation of Windows desktop client applications with an attractive user interface. For the aim of writing rich client applications WPF was introduced in the .NET Framework 3.0. Following points are the benefits of .NET WPF in comparison to Windows Forms:
- It supports advanced graphics, including free transformations, 3D rendering, multimedia capabilities, and true transparency. Appearance is supported through styles and templates;
- UIs can be described declaratively in XAML files. These files are maintained independently of the code-behind files, having the aim to help to separate appearance from functionality;
- It has flexible and extensive support for dynamic layout. It means that it is possible to localize the application without the danger of elements overlapping occurrence;
- The primary unit of measurement is not pixel-based, so apps render correctly at any DPI (dots per inch) setting;
- The rendering uses DirectX technology and is fast, taking advantage of the hardware-accelerated graphics;
- It offers reliable data binding.
Windows Forms
Windows Forms is a rich client API that is contemporary with the .NET Framework itself. Compared to WPF, it is a relatively simple technology that offers most of the capabilities needed when developing a typical Windows application. It also plays an important role in maintaining legacy applications. However, the Windows Forms framework has several disadvantages compared to WPF.
- The positions and sizes of controls are set in pixels, which leads to the risk of incorrect display of applications on clients with DPI settings that differ from those of the developer (although the situation has improved somewhat in the .NET Framework 4.7).
- Most of the controls do not support layout. For example, placing an image control inside the title of a tab control will fail. Customizing list views and drop-down boxes is time consuming and labor intensive.
- To draw custom controls, the GDI+ API is used, which, despite being quite flexible, renders large areas slowly (and can cause flickering without double buffering).
- The controls lack true transparency.
- It is difficult to get the dynamic layout to work reliably.
The last point is a good reason to choose WPF instead of Windows Forms, even if you are developing a business application that just needs a user interface rather than a “user behavior” consideration. Layout elements in WPF like Grid make it easy to organize labels and text boxes so that they are always aligned – even when changing languages localization - without messy logic or flickering. Plus, you don’t have to roll everything to the lowest common denominator in the terms of screen resolution — WPF layouts were designed from the ground up to be resizable. On a positive note, the Windows Forms framework is relatively easy to learn and is still supported in numerous third-party controls.
Xamarin
Xamarin is a leading open source platform for application development. It should be noted that Xamarin extends the .NET platform through libraries and tools. With its help developers build modern and productive native iOS, Android, watchOS, tvOS apps using .NET. Microsoft bought Xamarin in 2016 and it remains one of the most popular solutions for the .NET development of mobile applications.
How does Xamarin work and what is actually Xamarin? One of the main Xamarin advantages is the ability to write the C# code once and to reuse it on different platforms. In other words DB usage, business logic, network access and also other related functions are written by the developer only once and these parts are reused on each platform. In comparison to native iOS and native Android development it is much more beneficial from the business point of view and development costs. In case of native iOS/Android development customers actually pay for two different applications instead of one. Xamarin seems to be a much more feasible solution if the customer has a limited budget for the implementation of the application and short deadlines for realisation of this task. In general, Xamarin allows 80% of the application C# code to be used across multiple platforms.
Xamarin Native vs. Xamarin.Forms
Xamarin.Android and Xamarin.iOS are also called Xamarin Native or traditional Xamarin. In the classic approach in terms of Xamarin software development the applications have on the one hand shared access to the DBs and business logic. On the other hand, a distinct user interface is created for each operating system. Xamarin.Android and Xamarin.iOS help to create separate UIs. In lay terms, no common user interface is used here.
This approach is very beneficial as iOS and Android get native user interfaces. It helps to avoid possible occurrence of the issues like cut buttons and similar bugs. Each UI element is worked out taking into account the technical characteristics of the operating system. So, each component is built twice.
Along with the listed advantages of Xamarin Native business owners can still make a decision in favor of Xamarin.Forms. Xamarin.Forms allows developers to create user interfaces in eXtensible Application Markup Language (XAML). In case of Xamarin.Forms the application has a single design for both operating systems – iOS and Android.
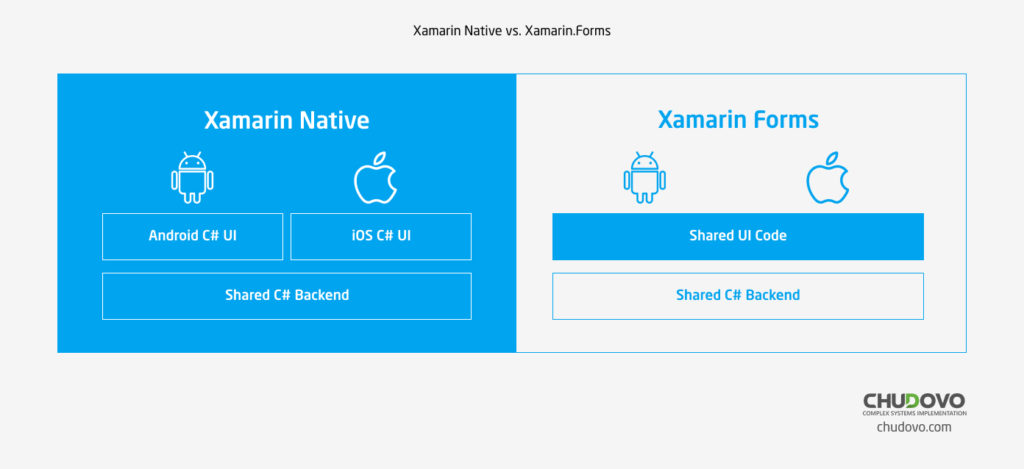
Xamarin Native or Xamarin.Forms – what is better to choose for application development?
Mainly the choice depends on business needs, budget for the development of the software, deadlines etc. Xamarin.Forms – this solution is well suited for those applications that include basic and well-known functions. For instance, messaging, media playback research/display of the information and other features. These screens will have more or less standard views. Maybe some cosmetical tuning will take place, but it is not critical. In this case Xamarin.Forms will be a good decision.
Xamarin Native – Xamarin.Android and Xamarin.iOS – provides more flexibility. If the application will have some specific functionality and custom feature development will be needed Xamarin Native is the best solution. Unique design for each OS, less issues in user interface – all these belong to its main advantages.
Xamarin end-of-life
Microsoft announced that Xamarin support ends on May 2024. Instead, Microsoft introduced .NET MAUI for the development of cross-platform applications. With the .NET MAUI developers can create desktop apps for Windows and MacOS as well as mobile apps for iOS and Android.
.NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI)
.NET MAUI framework is a good option for creation of native, mobile and cross-platform desktop apps. Native applications for MacOS, iOS, Android and Windows can be easily built with .NET MAUI. Single project approach and shared C# codebase are available with .NET MAUI.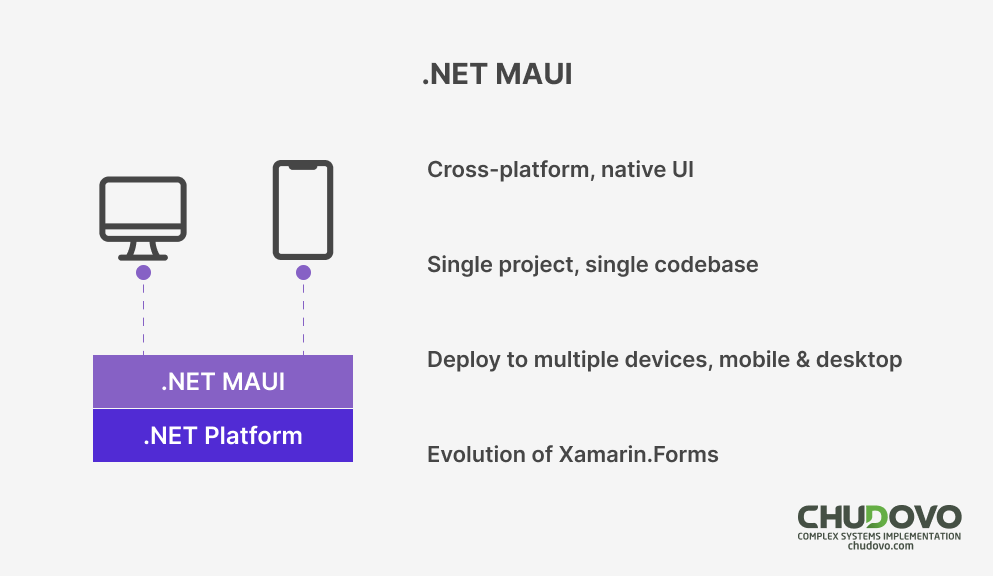
UWP (Universal Windows Platform)0
The Universal Windows Platform (UWP) is designed for developing apps targeting Windows 10 desktops and devices that are distributed through the Windows Store. Its rich client API, heavily influenced by the WPF framework, is designed to build touch-driven user interfaces and uses XAML for layout.
Silverlight
Silverlight allows to create graphical user interfaces that run in the web browser. It is very similar to Macromedia Flash. With the development of HTML5, Microsoft stopped focusing on Silverlight. Silverlight will be no longer supported starting from 12th of October, 2021.
Server-side technologies
Windows Workflow (.NET Framework only)
Windows Workflow is an infrastructure for modeling and managing potentially long-running business processes. The Windows Workflow focuses on the standard run-time library for consistency and interoperability. It also helps to reduce coding for dynamically managed decision trees. Windows Workflow Infrastructure is not strictly a server-side technology – it can be used anywhere (for example, a page flow in a user interface).
ADO.NET
ADO.NET is a Managed Data Access API. Although the name includes the name of ADO (ActiveX Data Objects), ADO.NET is a completely different technology. It contains two main low-level components.
Data provider is mainly used for the connection to the database, executing commands as well as retrieving results. The .NET Framework structure is provided with the support for Microsoft SQL Server, but many third-party drivers are available for other databases.
DataSet is a structured in-memory data cache. It resembles a primitive in-memory database that defines SQL constructs such as tables, columns, relationships, rows and views. By caching the data, server hits can be reduced, improving server scalability and rich client UI responsiveness. DataSet objects are serializable and can be passed over the network between client and server applications.
Data Access
Above Data Providers level, there are three APIs that offer the ability to query databases using LINQ:
- Entity Framework (.NET Framework only);
- Entity Framework Core (.NET Core and .NET Framework);
- LINQ to SQL (.NET Framework only).
All three technologies include object / relational mappers (ORMs), which automatically map objects (based on the classes you define) to rows in the database. This allows such objects to be queried using LINQ (instead of writing SQL SELECT statements) and updated without manually writing Insert / Delete / Update SQL statements. The result is less code inside the data access layer in the application (especially support code) and strong static type safety.
These technologies also eliminate the need for DataSets as repositories of data, although DataSets still offer the unique ability to store and serialize state changes (which is especially useful in multi-tier applications). Entity Framework or LINQ to SQL can be used in conjunction with the DataSet, although this approach is somewhat crude due to the awkwardness of the DataSet itself. In other words, there is still no straightforward out-of-the-box solution for writing n-tier applications with Microsoft’s ORM.
LINQ to SQL technology is simpler and faster than the Entity Framework, and has historically produced better SQL (although the Entity Framework has been improved through numerous updates). The Entity Framework is more flexible, because it allows to create precise mappings between the database and the queried classes (Entity Data Model), and offers a model that enables independent support for databases other than SQL Server.
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) is a rewritten Entity Framework with a simpler LINQ to SQL inspired design solution. It ditches the complex entity data model and runs under the .NET Framework and .NET Core.
Distributed Systems Technologies
Remoting and .ASMX Web Services (.NET Framework only)
Remoting and .ASMX Web Services are the predecessors of WCF. With the advent of WCF, Remoting technology has become almost superfluous, and .ASMX Web Services – entirely superfluous. Remaining niche Remoting concerns communication between application domains within the same process. Remoting is targeted at applications with strong connectivity. A typical example would be when the client and server are .NET applications written by the same company (or companies that share common assemblies). Communication typically involves the exchange of potentially complex .NET special objects that the Remoting framework serializes and deserializes without the need for external intervention.
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF)
WCF is a sophisticated infrastructure for communications that was introduced in the .NET Framework 3.0. It is configurable enough and very flexible and to make its predecessors Remoting and Web Services (.ASMX) less needed. WCF, Remoting and Web Services are similar in that they all implement the basic communication model described below between client and server applications:
- On the server side, you specify which methods can be called by remote client applications.
- On the client side, you specify or display the signatures of the server methods to be called.
- On the server and client sides, you choose the transport and communication protocol (in WCF this is done through a binding).
- The connection to the server is actually established by the client.
- The client calls a remote method, which runs transparently on the server.
WCF infrastructure further decouples the client and server through data and service contracts. Conceptually, instead of directly calling the remote method, the client sends a message (XML or binary) to the remote service endpoint. One of the benefits of this decoupling is that clients don’t have the dependencies on the .NET platform as well as on any proprietary communication protocols.
WCF is highly configurable and offers broad support for standardized messaging protocols based on Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP). The result is the ability to interact with contributors running other software – likely on different platforms – while still supporting advanced features like encryption. In practice, however, the complexity of these protocols limits their adoption by other platforms, and currently the best choice for interoperable messaging is the REST over HTTP architectural style, which Microsoft supports through the ASP.NET-based Web API layer.
However, for communication between .NET systems, WCF offers more advanced serialization and better tools than those available with REST APIs. It is also potentially faster, is not tied to HTTP, and can use binary serialization.
Web API (ASP.NET/ASP.NET Core)
Web API is architecturally similar to Microsoft’s MVC API, except that it is designed to expose access to the services and data rather than to the web pages. The advantage of Web API infrastructure in contrast to WCF is that it allows to follow popular REST conventions over HTTP, offering uncomplicated interoperability across a wide range of platforms. Internally, REST implementations are simpler than the SOAP protocols that WCF relies on for interoperability. Architecturally, REST APIs are more elegant for loosely coupled systems, built on based on de facto standards and makes excellent use of what the HTTP protocol already provides.
Other technologies
Unity
Unity is a real-time 3D development platform that is intended for the creation of 2D as well as 3D applications such as games or simulations, using .NET and of course the C# programming language. Unity is the world’s leading platform that allows developers, artists and designers to work together in order to produce amazing interactive user experiences. Produced games and simulations can be launched on 25+platforms across web, desktop, mobile, consoles (Nintendo Switch, PlayStation, Xbox, Google Stadia) AR, VR, TV etc. Initially, Unity engine was provided by Unity Technologies, an American video game development company. This firm has started a cooperation with Microsoft in the direction of tools development.
.NET Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Implementation of the intelligent applications with the unique features like emotions or sentiments detection, language understanding, visual speech recognition is no longer fiction, but nowadays reality. Undoubtedly, such a software can be easily built on .NET.
ML.NET is a machine learning framework, open-source and cross-platform, produced specially for the .NET developers. Custom ML models can be integrated into the .NET apps, without need in prior machine learning experience.
ML.NET allows to add machine learning capabilities to the .NET applications in online or offline scenarios. By using this feature, developer has an ability to make and to receive automatic predictions based on the data available to your application. Machine learning applications use the standard patterns in the data to predict the events without need in being explicitly programmed. Microsoft ML.NET is based on the machine learning model. This model defines the steps that should be done to receive the predictions based on the input data. Surely, with ML.NET the developer can train a custom model by specifying an appropriate algorithm as well as it is possible to import pretrained ONNX and TensorFlow models. The generated model can be added to the application and used to generate predictions.
Custom ML models can be created using F# or C# for the variety of machine learning scenarios without leaving the .NET ecosystem. ML.NET gives an opportunity to reuse and to apply the knowledge, qualifications, libraries, code that person already has as .NET dev. Software engineer without a doubt having this technical basis will be able to integrate ML into mobile, desktop, web solutions as well IoT applications and games.
.NET IoT Apps
.NET is also used for the aim of building IoT systems. It’s cross-platform and is able to support several input devices, displays as well as sensors that use PWM, SPI, I2C, GPIO and of course serial port interfaces. Devices have gas and humidity sensors, RFID/NFC modules, DHT temperature, accelerometers etc. Adafruit Seesaw, GrovePi, Sense HAT are complex hats that are supported. .NET IoT Library helps in creation of the applications that run on BeagleBoard, Pine A64 Raspberry Pi, HummingBoard etc. Special adapters may even transform the Mac or PC into the IoT device.


No comments:
Post a Comment